HOME > Research > Mott transition
Mott transition
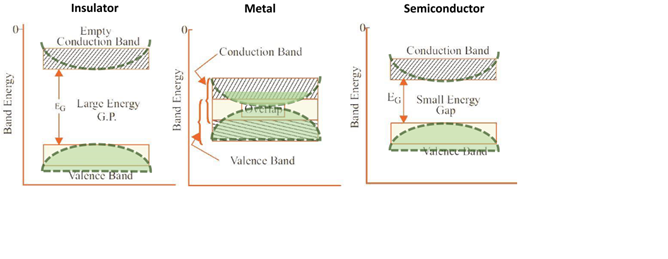
기존의 밴드이론에 따르면 전자는 입자로서 생각되어 다른 전자와 독립적으로 위치한 주기적인potential 내를 움직이게 된다. 이 때 에너지 밴드는 각 원자들의 오비탈 중첩에 의해 생성되는데 위 그림과 같이 밴드내에 전자들이 부분적으로 차 있을 경우 metal로 분류되며그렇지 않은 경우 insulator로 분류되곤 한다.
하지만 3d, 4d 혹은 4f 오비탈에 전자가 존재하는 transition metal oxide의 경우, 위와 같은 방식으
로 기존 밴드이론에 따라 metal로 구분되어야할 물질이 실제로는 insulator한
상황이 발생하였다. 이러한 물질을 Mott insulator라고
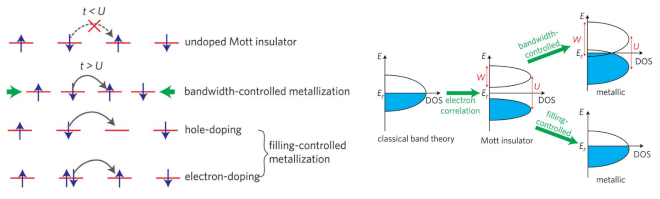
부르며 전자간의 Coulomb repulsion 에너지로 인하여 U라는
에너지 간격이 생기게 되고 전자들이 가진 운동에너지 t가 U보다
큰 상황일 경우에만 전자가 이동할 수 있다.

<Zhou,
You, and Shriram Ramanathan. "Mott memory and neuromorphic
devices." Proceedings of the IEEE 103.8 (2015):
1289-1310.>
Mott insulator는 lattice의 strain을 유발하여 원자간의 오비탈 간격을 좁혀 bandwidth를 조절하는 bandwidth-controlled 방법과 다른 물질을 doping하여 energy band를 변화시키는
filling-controlled 방법을 통해 Insulator Metal Transition(MIT)를 가능하게 만들 수 있다.
<Catalano,
Sara, et al. "Rare-earth nickelates RNiO3: Thin films and
heterostructures." Reports on Progress in Physics 81.4
(2018): 046501.>
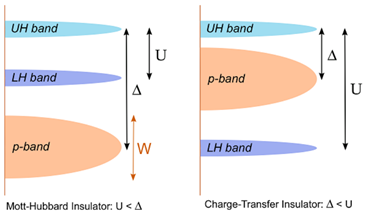
Mott transition oxide는
d 밴드에 위치하는 전자 repulsion에 따라 종류가 두가지로 나뉘게 된다. 처음 설명한 바와 같이 transition metal 내의 전자간의
repulsion으로 인하여 Coulomb interaction에너지 U가 생
성된다. 이를 Lower Hubbard(LH)와 upper Hubbard(UH) 밴드로 나타내며 이 사이에 에너지 갭을 U라 표기한다.
그리고 산소가 갖는 p band와의 차이를 △라 하였을 때 U>△를 가지는
이러한 물질을 Mott-
Hubbard Insulator라 하며 VO2와 같은 물질에 해당된다.
다.
반면에 Ni, Cu와 같이 heavy transition metal의 경우 많은 전자로 인해 d-d interaction 뿐만 아니라 산소가 가지는 p band와 interaction이 발생하여
p-band의 에너지 밴드가 UH와 LH 밴드 사이에 위치하게 된다. 이와 같이 U>△인 경우의
물질을 Charge-Transfer Insulator라 부른다.
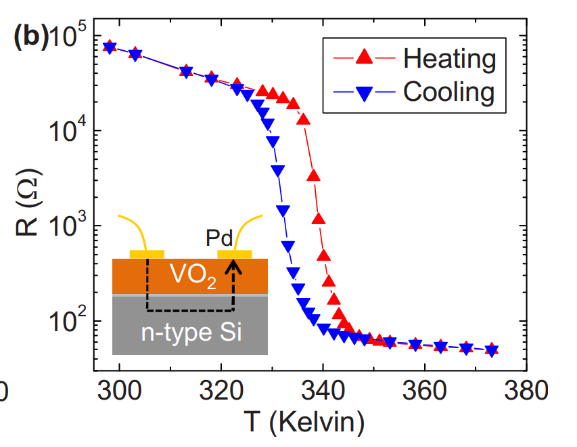
Mott insulator에서 Temperature-Controlled
IMT(VO2, NbO2, Ca2RuO4 etc)와 Filling controlled IMT(La2CuO4, Pr0.7Ca0.3MnO3,
NiO etc) 방식의 저항 스위칭 방식의 메모리가 연구되어 왔으며 기존
ReRAM과 같이
3D cross point array 기술을 통해 대용량 구현이 가능하다.

<Kim, Jeehoon, et al.
"Nanoscale imaging and control of resistance switching in VO 2 at room
temperature." Applied Physics Letters 96.21 (2010):
213106.>
<Liao, Z. L., et al. "Categorization of
resistive switching of metal-Pr 0.7 Ca 0.3 MnO 3-metal devices." Applied
Physics Letters 94.25 (2009): 253503.>

